IRA Environmental Impact: 15 Key Changes 2024-2025

The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is significantly reshaping environmental policy, introducing 15 key changes for 2024-2025 with substantial financial impacts and recent updates to accelerate clean energy and emissions reductions.
The Inflation Reduction Act’s Environmental Policy Impact: 15 Key Changes for 2024-2025 (FINANCIAL IMPACT, RECENT UPDATES) is rapidly transforming the landscape of climate action and clean energy development across the United States. As of early 2024, new guidance and implemented programs are detailing how this landmark legislation is translating into tangible environmental benefits and significant financial shifts for businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding the IRA’s Core Environmental Mandate
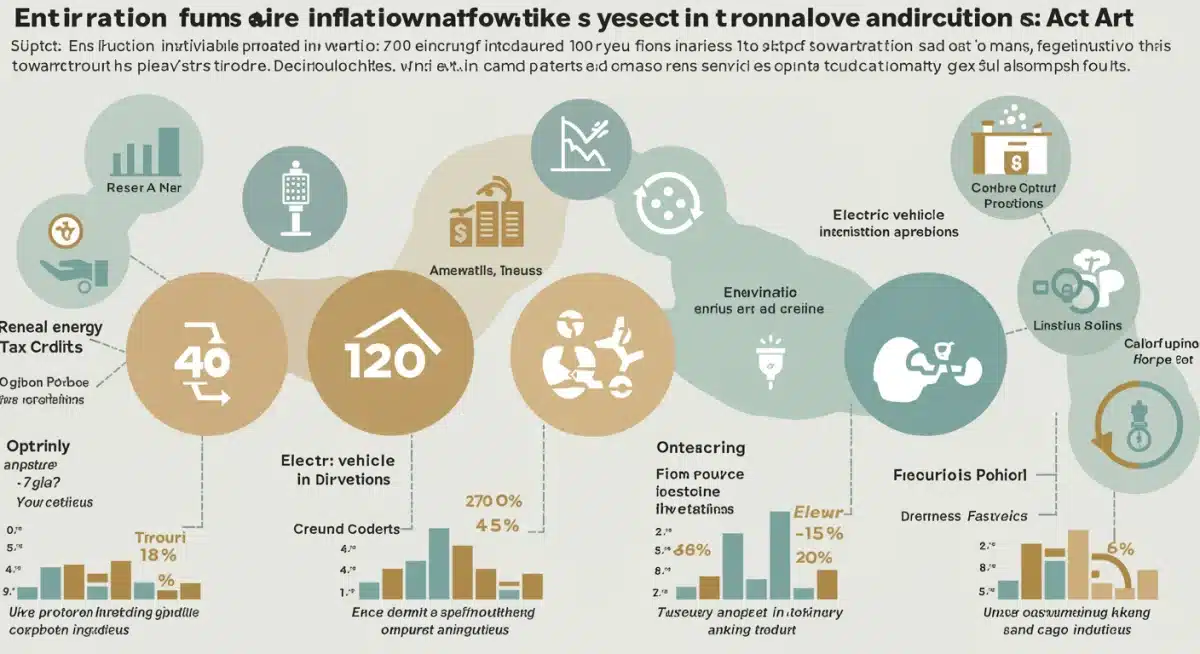
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), signed into law in August 2022, represents the most significant climate legislation in U.S. history. Its core environmental mandate is to drastically reduce carbon emissions, promote clean energy technologies, and enhance environmental justice initiatives. The Act allocates hundreds of billions of dollars through tax credits, rebates, and grants, aiming to cut U.S. emissions by approximately 40% below 2005 levels by 2030, according to government projections.
This legislative push is not merely about environmental protection; it’s a strategic economic move designed to stimulate domestic clean energy manufacturing and create jobs. Recent updates from the Department of Energy and Treasury Department clarify eligibility criteria and implementation timelines for various programs, ensuring that the financial incentives are accessible and effective in driving the green transition.
Accelerated Renewable Energy Deployment
A primary focus of the IRA is to accelerate the deployment of renewable energy sources. This includes expanding existing tax credits and introducing new ones to make solar, wind, geothermal, and other clean energy technologies more competitive and widespread. The goal is to rapidly increase the grid’s capacity for clean power generation, moving away from fossil fuels.
- Extension and expansion of the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for solar and wind projects.
- Introduction of new production tax credits (PTCs) for clean electricity generation.
- Incentives for energy storage technologies, crucial for grid stability with intermittent renewables.
- Bonus credits for projects that meet domestic content requirements or are located in energy communities.
Key Financial Incentives Driving Clean Energy Transition
The financial incentives within the IRA are extensive, designed to encourage both large-scale industrial projects and individual household adoption of clean energy. These incentives are critical for achieving the Act’s ambitious emissions reduction targets and are now actively shaping investment decisions across various sectors. The focus on long-term, stable tax credits provides certainty for investors and developers, fostering a robust clean energy economy.
As of recent announcements, several Treasury Department guidance documents have provided clarity on how businesses and individuals can claim these credits, streamlining the application process and increasing participation rates. This clarity is vital for maximizing the impact of these financial tools.
Residential Clean Energy Credits
Homeowners are seeing significant benefits through expanded tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements and renewable energy installations. These provisions are designed to reduce household energy costs and promote sustainable living.
- 30% tax credit for residential clean energy products like solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heat pumps.
- Tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements, including new windows, doors, insulation, and HVAC systems.
- Rebates for electric appliances and home energy audits, making green upgrades more affordable.
Impact on Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure
The IRA significantly boosts the electric vehicle (EV) market and its supporting infrastructure, aiming to reduce transportation emissions. This includes consumer tax credits for new and used EVs, as well as substantial investments in charging networks. The goal is to make EVs more accessible and practical for a broader segment of the population, accelerating the transition away from gasoline-powered vehicles.
Recent developments include stricter battery component sourcing requirements that impact which vehicles qualify for the full tax credit, as well as new funding allocations for state and local governments to build out public charging stations. These measures are critical for addressing range anxiety and supporting mass EV adoption.
Consumer EV Tax Credits
For consumers, the Act offers considerable financial incentives to purchase electric vehicles, both new and pre-owned, playing a crucial role in making EVs a mainstream option.
- Up to $7,500 tax credit for new clean vehicles, subject to battery sourcing and manufacturing location requirements.
- Up to $4,000 tax credit for used clean vehicles, making EVs more affordable for a wider demographic.
- Exemption of commercial vehicles from some sourcing requirements, encouraging fleet electrification.
Advancements in Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
The IRA provides substantial new incentives for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies, recognizing their potential role in decarbonizing hard-to-abate industrial sectors. This includes enhanced tax credits for facilities that capture carbon emissions, encouraging both technological innovation and commercial deployment. The objective is to mitigate emissions from heavy industries that cannot easily transition to renewable energy sources.
As of late 2023 and early 2024, the Department of Energy has announced several funding opportunities and demonstration projects related to CCUS, leveraging the IRA’s provisions. These initiatives are crucial for scaling up the technology and addressing the technical and economic challenges associated with large-scale carbon capture.
Enhanced Tax Credits for CCUS
The Section 45Q tax credit for CCUS has been significantly increased and expanded, making these projects more financially viable and attractive for industrial players.
- Increased tax credit for direct air capture (DAC) projects to $180 per metric ton.
- Higher credit for carbon capture from industrial sources and power plants, now up to $85 per metric ton.
- Expanded eligibility for smaller-scale projects, broadening the reach of CCUS technology.
Strengthening Environmental Justice Initiatives
A critical component of the IRA is its focus on environmental justice, ensuring that the benefits of clean energy and climate investments reach historically disadvantaged communities. The Act includes specific provisions and bonus credits for projects located in low-income or energy-transition communities, aiming to address decades of environmental inequity. This commitment is central to a holistic approach to climate action, ensuring that all communities benefit from the green transition.
Recent federal announcements highlight new grant programs and technical assistance initiatives specifically tailored for these communities, facilitating their access to IRA funding. This proactive approach aims to prevent the perpetuation of environmental burdens and promote equitable development.
Targeted Community Investments
The IRA directs funds and incentives towards communities that have disproportionately borne the brunt of pollution and economic challenges from fossil fuel industries.
- Bonus tax credits for clean energy projects located in low-income communities or areas impacted by fossil fuel closures.
- Creation of a Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund to provide financial and technical assistance to community-based nonprofits.
- Funding for clean energy and climate resilience projects in tribal communities and territories.
Promoting Domestic Manufacturing and Supply Chains
Beyond direct environmental benefits, the IRA strongly emphasizes boosting domestic manufacturing of clean energy technologies. This includes battery components, solar panels, wind turbine parts, and critical minerals processing. The goal is to create a robust U.S. clean energy supply chain, reducing reliance on foreign sources and creating high-paying jobs within the country. This strategic focus is crucial for national energy security and economic resilience, as highlighted by recent geopolitical events.
New guidance on domestic content bonuses has spurred significant investment announcements from manufacturers looking to capitalize on these incentives. This is leading to a resurgence in American manufacturing, particularly in sectors vital for the green economy.
Incentives for U.S. Production
The Act provides substantial tax credits and incentives for companies that manufacture clean energy components and vehicles within the United States, fostering a resilient domestic supply chain.
- Advanced Manufacturing Production Tax Credit (45X) for components like solar cells, wind turbine blades, and battery materials.
- Bonus credits for EV manufacturers that source a certain percentage of battery components and critical minerals from the U.S. or free-trade partners.
- Grants and loans to support the modernization and expansion of domestic clean energy manufacturing facilities.
| Key Change | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Credits | Expanded tax credits for solar, wind, and other clean electricity generation and storage. |
| EV Tax Incentives | New and used electric vehicle tax credits with domestic sourcing requirements. |
| Carbon Capture Boost | Significantly enhanced Section 45Q tax credits for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage. |
| Domestic Manufacturing | Incentives for U.S. production of clean energy components and critical minerals. |
Frequently Asked Questions About the IRA’s Environmental Impact
The IRA’s primary environmental goal is to reduce U.S. carbon emissions by approximately 40% below 2005 levels by 2030. It achieves this through substantial investments and incentives for clean energy, electric vehicles, and emissions reduction technologies across various sectors, aiming for a significant shift towards a greener economy.
Homeowners can receive a 30% tax credit for installing residential clean energy products like solar panels and geothermal heat pumps. Additionally, credits are available for energy-efficient home improvements such as new windows, insulation, and heat pumps, reducing upfront costs and promoting sustainable living practices nationwide.
Yes, new requirements for EV tax credits, up to $7,500 for new vehicles and $4,000 for used, now include stricter battery component sourcing and critical mineral extraction criteria. Vehicles must meet these domestic content thresholds to qualify for the full credit, promoting a U.S.-centric supply chain.
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) are crucial for decarbonizing heavy industrial sectors. The IRA significantly enhances the Section 45Q tax credit, increasing incentives for direct air capture to $180/metric ton and industrial capture to $85/metric ton, making CCUS projects more economically viable and widespread.
The IRA includes specific provisions and bonus credits for clean energy projects in low-income communities and areas historically impacted by fossil fuel industries. It also establishes a Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund to support community-based climate initiatives, aiming to ensure equitable distribution of environmental and economic benefits.
Looking Ahead
The Inflation Reduction Act’s environmental policy impact is a dynamic and evolving story. As 2024 progresses into 2025, we anticipate further guidance from federal agencies, continued investment announcements, and the tangible realization of emissions reductions. The interplay between industry, government, and communities will be crucial in maximizing the Act’s potential. Observers should watch for the long-term effects on energy prices, job growth in the green sector, and the overall trajectory of U.S. climate goals. The coming months will provide clearer insights into the extent of this transformative legislation’s success in forging a sustainable future.