EPA Methane Rules 2026: U.S. Industry Compliance Guide
Latest developments on EPA Methane Rules 2026, with key facts, verified sources and what readers need to monitor next in Estados Unidos, presented clearly in Inglês (Estados Unidos) (en-US).
Navigating the New EPA Methane Emissions Rules: A 2026 Compliance Guide for U.S. Industries is shaping today’s agenda with new details released by officials and industry sources. This update prioritizes what changed, why it matters and what to watch next, in a straightforward news format.
Understanding the New EPA Methane Rules 2026 Framework
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has finalized stringent new rules aimed at reducing methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry. These regulations, set to take full effect by 2026, represent a significant step in the nation’s climate strategy.
Industry stakeholders are now grappling with the specifics of these rules, which mandate enhanced leak detection and repair (LDAR) programs, stricter equipment standards, and comprehensive reporting requirements. The goal is to curb methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from sources across the production and processing lifecycle.
This regulatory push underscores a broader commitment to environmental stewardship and climate change mitigation. Companies operating within the oil and gas sector must proactively assess their operations and develop robust compliance strategies to meet the impending deadlines.
Key Components of the EPA Methane Rules 2026
The new regulations introduce several critical measures designed to minimize methane leakage and venting. These components touch upon various operational aspects, requiring a holistic approach to compliance.
A central tenet is the requirement for more frequent and advanced leak detection. This includes the use of optical gas imaging (OGI) technology and other innovative methods to identify and repair leaks promptly, moving beyond less effective traditional practices.
Furthermore, the rules address specific equipment types, mandating upgrades or replacements for high-emitting pneumatic controllers, pumps, and compressors. These provisions aim to tackle known sources of significant methane releases, ensuring better operational integrity.
Enhanced Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR)
The EPA’s updated LDAR requirements are more rigorous than previous standards, demanding regular inspections and swift repairs. Companies must implement systematic programs to detect and fix leaks across their infrastructure.
This includes not only production sites but also gathering and boosting stations, processing plants, and transmission and storage facilities. The scope is broad, reflecting the EPA’s intent to address emissions comprehensively from wellhead to consumer.
- Mandatory quarterly or semi-annual inspections for most facilities.
- Requirement to use advanced OGI technology for leak detection.
- Strict deadlines for repairing identified leaks, categorized by severity.
Equipment Standards and Controls
The rules set new performance standards for various equipment, particularly targeting pneumatic controllers and pumps. Many existing devices will need to be replaced or retrofitted to meet these more stringent emission limits.
New and modified sources will face even stricter requirements, encouraging the adoption of best available technologies from the outset. This forward-looking approach aims to prevent future emissions rather than just mitigating existing ones.
For example, pneumatic controllers will largely need to be zero-emission for new installations and low-bleed for existing ones, significantly reducing continuous methane releases. This is a crucial aspect of the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Compliance Deadlines and Phased Implementation
While the full force of the EPA Methane Rules 2026 will be felt by 2026, the implementation is phased, with different requirements coming into effect at various stages. Understanding this timeline is essential for strategic planning.
Some provisions, particularly those related to new and modified sources, are already in effect or will be soon. Existing sources generally have more time to comply, but preparations should begin immediately to avoid last-minute rushes.
The EPA has structured the rollout to allow industries time to adapt, invest in new technologies, and train personnel. However, this grace period is not an excuse for inaction but an opportunity for proactive engagement with the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Initial Compliance Requirements (2024-2025)
Early phases of the regulations focus on establishing foundational reporting and monitoring practices. Companies must begin to collect and submit data according to new formats and frequencies.
This period also involves initial assessments of existing infrastructure to identify areas needing upgrades or modifications. Early identification of compliance gaps can prevent costly remediation later.
- Baseline emissions reporting and inventory updates.
- Initial assessments of pneumatic devices and compressors.
- Development of LDAR plans tailored to new EPA standards.
Full Compliance by 2026
By 2026, all regulated facilities, both new and existing, must be in full compliance with the updated standards. This includes the complete implementation of enhanced LDAR programs and the retrofitting or replacement of non-compliant equipment.
Companies that fail to meet these deadlines risk significant penalties, including fines and operational restrictions. The EPA has indicated a firm stance on enforcement to ensure the effectiveness of the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
The lead-up to 2026 will be a critical period for investment in technology, workforce training, and process optimization. The complexity of EPA Methane Rules 2026 necessitates a detailed, multi-year compliance roadmap.

Impact on U.S. Industries and Economic Considerations
The new EPA Methane Rules 2026 will have far-reaching implications for various sectors within the U.S. economy, particularly the oil and natural gas industry. These impacts extend beyond direct compliance costs to broader economic considerations.
While compliance will require significant capital investment in new equipment and technologies, it also presents opportunities for innovation and efficiency improvements. Reduced methane leaks can translate into less product loss, potentially offsetting some costs.
Furthermore, meeting these standards can enhance a company’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) profile, attracting investors and consumers who prioritize sustainability. This is a critical factor for long-term viability under the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Financial Implications for Operators
Operators, especially smaller independent companies, may face substantial financial burdens in upgrading infrastructure and implementing new protocols. Access to capital and understanding available incentives will be crucial.
Larger corporations may have more resources to absorb these costs, but all entities will need to carefully manage their budgets and prioritize investments. The long-term benefits of compliance are expected to outweigh the initial expenditures.
The EPA Methane Rules 2026 will necessitate a re-evaluation of current operational expenditures and capital allocation strategies. Financial planning is paramount for successful adaptation.
Technological Advancements and Job Creation
The demand for advanced methane detection and abatement technologies is expected to surge, driving innovation in the environmental technology sector. This could lead to the creation of new jobs in manufacturing, research, and specialized services.
Companies that develop and deploy these solutions stand to benefit significantly. The emphasis on OGI and other high-tech detection methods will foster a new ecosystem of specialized service providers.
This technological shift represents a positive economic externality of the EPA Methane Rules 2026, stimulating growth in specific segments of the economy while addressing environmental concerns.
Strategies for Effective Compliance with EPA Methane Rules 2026
To successfully navigate the new regulatory landscape, U.S. industries must adopt proactive and strategic approaches. A comprehensive compliance plan is not merely about meeting minimum requirements but about integrating environmental stewardship into core business operations.
This involves a multi-faceted strategy encompassing technological upgrades, process optimization, employee training, and robust data management. Early engagement and continuous monitoring are key to avoiding compliance pitfalls.
Companies should consider forming cross-functional teams dedicated to overseeing EPA Methane Rules 2026 implementation, ensuring that all relevant departments are aligned and informed.
Developing a Comprehensive Compliance Plan
A detailed plan should outline specific actions, timelines, responsible parties, and budget allocations for each aspect of the rules. This includes inventorying existing equipment, identifying non-compliant assets, and scheduling upgrades.
The plan should also incorporate a robust LDAR program, including the selection of appropriate technologies and the establishment of regular inspection schedules. Documentation and record-keeping are critical components.
- Conduct a thorough baseline assessment of current emissions and equipment.
- Identify gaps between current practices and new EPA requirements.
- Allocate resources for technology acquisition, retrofitting, and personnel training.
Leveraging Technology and Innovation
Adopting advanced methane detection and reduction technologies can streamline compliance efforts and improve efficiency. Investing in cutting-edge solutions can provide a competitive advantage.
This includes continuous monitoring systems, remote sensing capabilities, and data analytics platforms that can track emissions, identify trends, and predict potential issues. Technology is a powerful ally in meeting the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Exploring partnerships with technology providers and research institutions can also accelerate the adoption of innovative solutions, ensuring that companies remain at the forefront of emission control.
Role of Data Management and Reporting
Accurate and transparent data management is paramount under the new EPA Methane Rules 2026. The EPA requires detailed reporting on emissions, leak detection activities, and repair outcomes.
Companies must establish robust systems for collecting, storing, and analyzing this data to demonstrate compliance effectively. Poor data management can lead to reporting errors, potential non-compliance, and regulatory scrutiny.
Investing in specialized software and training personnel in data handling protocols will be essential. The integrity of reported data directly reflects a company’s commitment to the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Streamlining Data Collection and Analysis
Implementing digital tools for field data collection can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency. Mobile applications and integrated sensor networks can provide real-time information on emission sources and repair statuses.
Centralized data platforms can then aggregate this information, allowing for comprehensive analysis and identification of performance trends. This data-driven approach supports continuous improvement.
- Utilize digital platforms for consistent data entry and storage.
- Implement analytics tools to identify emission hotspots and patterns.
- Ensure data is auditable and readily accessible for EPA inspections.
Transparent Reporting Practices
The EPA mandates regular submission of emissions data and compliance reports. Companies must ensure their reporting mechanisms are robust, accurate, and submitted within specified deadlines.
Transparency in reporting not only fulfills regulatory obligations but also builds trust with stakeholders, including investors, communities, and environmental groups. This transparency is a cornerstone of the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Clear, concise, and verifiable reports are essential for demonstrating good faith efforts and adherence to the spirit and letter of the regulations. This minimizes the risk of enforcement actions.
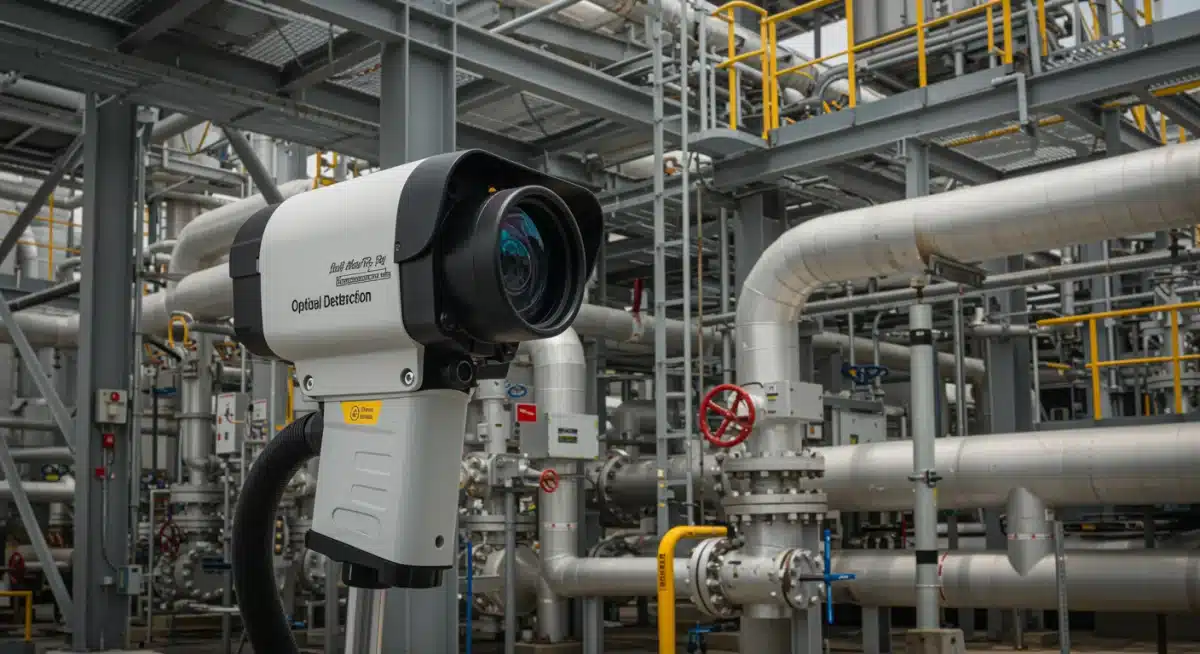

Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
While the EPA Methane Rules 2026 aim to achieve significant environmental benefits, their implementation is not without challenges. Industries may encounter hurdles related to costs, technological integration, and workforce readiness.
One primary challenge is the capital expenditure required for equipment upgrades and new technologies. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may find this particularly difficult without adequate financial support or incentives.
Another area of concern is the availability of skilled labor to operate and maintain new detection equipment and implement complex LDAR programs. Workforce development and training will be critical mitigation strategies.
Addressing Cost and Financial Strain
Companies should explore federal and state incentive programs, grants, and tax credits designed to support methane emission reductions. These programs can help offset a portion of the compliance costs.
Strategic phasing of investments can also help manage financial strain, prioritizing the most impactful or mandated upgrades first. Long-term budgeting should account for ongoing maintenance and operational costs associated with compliance.
Collaboration within industry associations to share best practices and collectively lobby for supportive policies can also mitigate financial burdens related to the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Workforce Training and Skill Development
The demand for technicians skilled in OGI, sensor deployment, and data analysis will increase significantly. Companies must invest in training their existing workforce or recruiting new talent with these specialized skills.
Partnerships with educational institutions and vocational schools can help develop curricula tailored to the needs of the industry under the new regulations. This ensures a pipeline of qualified professionals.
Ongoing professional development programs will be necessary to keep pace with evolving technologies and regulatory updates, ensuring sustained compliance with the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
The Future of Methane Regulation Beyond 2026
The EPA Methane Rules 2026 are part of a larger, evolving regulatory landscape aimed at addressing climate change. Industries should view these rules not as a static endpoint but as a dynamic benchmark that will likely be refined and expanded in the future.
Policymakers may introduce further restrictions or expand the scope to other sectors as technology advances and climate goals become more ambitious. Continuous adaptation and foresight will be essential.
Staying informed about emerging research, technological breakthroughs, and international climate agreements will enable U.S. industries to anticipate future regulatory shifts and maintain a competitive edge.
Anticipating Further Regulatory Evolution
The EPA regularly reviews and updates its environmental standards based on scientific advancements and policy objectives. Companies should expect future iterations of methane regulations that may introduce stricter limits or new compliance mechanisms.
The focus could expand to include other potent greenhouse gases or incorporate novel monitoring and verification technologies. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies can help shape these future policies.
- Monitor EPA announcements and proposed rule changes closely.
- Engage in industry dialogues and public comment periods.
- Invest in research and development for next-generation emission control.
Global Context and U.S. Leadership
The U.S. role in methane reduction is also viewed within a global context, influencing international climate negotiations and standards. Strong domestic regulations reinforce the nation’s commitment to climate action.
This leadership can also open up opportunities for U.S. companies to export their expertise and technologies in methane abatement to other countries. The EPA Methane Rules 2026 contribute to this global effort.
Understanding these broader implications can help U.S. industries position themselves as leaders in sustainable energy production and environmental management, aligning with global climate goals.
| Key Requirement | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced LDAR | Mandatory, frequent leak detection and repair using advanced technologies. |
| Equipment Standards | Upgrades or replacements for high-emitting pneumatic devices and compressors. |
| Reporting & Data | Comprehensive data collection and transparent submission of emissions reports. |
| 2026 Deadline | Full compliance for all regulated facilities by the specified year. |
Frequently Asked Questions on EPA Methane Rules 2026
The primary goals are to significantly reduce methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry, a potent greenhouse gas, to combat climate change. These rules aim to enhance public health and environmental quality by curbing harmful air pollutants and promoting sustainable operational practices across the sector in the U.S.
The oil and natural gas industry is most directly affected, encompassing producers, processors, and transporters of oil and gas. Facilities involved in exploration, production, gathering, boosting, processing, and transmission are all subject to the new requirements for the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Key technologies include Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) cameras for leak detection, advanced sensors for continuous monitoring, and low- or zero-emission pneumatic controllers and pumps. Companies must also invest in robust data management systems to track and report emissions accurately under the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
Yes, federal and state governments may offer various incentive programs, grants, and tax credits designed to support industries in adopting methane reduction technologies and practices. Companies are encouraged to research and apply for these programs to help offset compliance costs associated with the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
The EPA will enforce the regulations through rigorous inspections, mandatory reporting, and potential penalties for non-compliance, including fines and operational restrictions. The agency emphasizes a data-driven approach, relying on accurate reporting and documented LDAR activities to ensure adherence to the EPA Methane Rules 2026 standards.
Looking Ahead: Sustained Compliance and Innovation
The EPA Methane Rules 2026 mark a pivotal moment for U.S. industries, particularly the oil and natural gas sector. The shift towards more stringent environmental standards is not merely a regulatory burden but an impetus for innovation and operational excellence. Companies that embrace these changes proactively will not only ensure compliance but also position themselves as leaders in a rapidly evolving energy landscape.
The ongoing commitment to reducing methane emissions will require continuous investment in technology, robust training programs, and adaptive management strategies. The long-term benefits, including enhanced public trust, reduced product loss, and a stronger ESG profile, underscore the importance of this transition. This comprehensive approach ensures industries thrive under the EPA Methane Rules 2026.
As the 2026 deadline approaches, vigilance and strategic planning will be paramount. The EPA will likely continue to refine and expand its environmental policies, making sustained engagement with regulatory developments a critical component of future business success. The journey to full compliance with the EPA Methane Rules 2026 is an ongoing process of improvement.